There are no items in your cart
Add More
Add More
| Item Details | Price | ||
|---|---|---|---|

The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of India and is responsible for implementing monetary policy in the country. Monetary policy refers to the measures taken by the central bank to control the money supply and interest rates in the economy, with the goal of achieving price stability and fostering economic growth.
What are the parameters included in monetary policy?
The RBI conducts monetary policy through a variety of tools, including changes in the repo rate, cash reserve ratio (CRR), and statutory liquidity ratio (SLR). The repo rate is the interest rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks, while the CRR and SLR are the percentage of deposits that banks are required to keep with the RBI. By changing these rates, the RBI can influence the amount of money that banks have available to lend, and therefore, the overall level of economic activity in the country.
How does the monetary policy affect us?
One of the key objectives of the RBI's monetary policy is to control inflation. In order to do this, the RBI regularly assesses the state of the economy and sets its monetary policy stance accordingly. If inflation is high, the RBI may increase the repo rate or the CRR to tighten monetary policy and reduce inflationary pressures. As the rates rise, loans will get expensive and deposits will get attractive. This will lead to less money in the hands of people to spend. Lower spending will lead to lower demand thereby reducing prices and inflation. On the other hand, if inflation is low, the RBI may decrease the repo rate or reduce the CRR to stimulate economic growth.
The RBI's monetary policy also plays a crucial role in promoting financial stability in the country. For example, during periods of financial turmoil, the RBI may take steps to provide liquidity to the financial system and ensure that banks have access to funding. This helps to prevent financial instability from spreading and causing wider economic damage.
In the chart below we can see that during the Covid-19 pandemic, RBI reduced the rates to increase the flow of money into the hands of people.
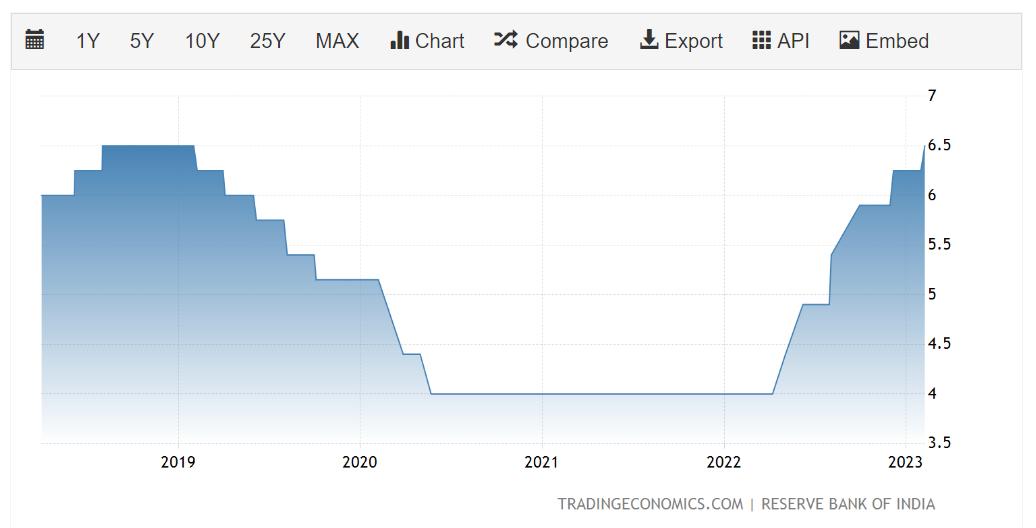
What factors cause a change in Monetary policy?
The RBI's Monetary Policy Committee is required to meet at least four times a year. The monetary policy is guided by several important considerations, including inflation expectations, economic growth, and the state of the global economy. The RBI also takes into account the views and expectations of various stakeholders, including the government, commercial banks, and financial market participants.
In conclusion, the RBI's monetary policy plays a crucial role in shaping the economic landscape of India. By carefully balancing the goals of price stability and economic growth, the RBI helps to create a stable and sustainable environment for economic activity in the country. Whether you're an investor, a business owner, or simply an interested observer, it's important to pay close attention to the RBI's monetary policy and how it may impact the economy.
If you want to stay updated on such events connect to the Thursday evening Live Streams on my channel, where I discuss various macroeconomic events, and where is the market headed for the week through technical analysis and option chain analysis. Until then…